Food and Health Communications aims to educate, empower, and inspire health practitioners around the globe to help their clients make the best food choices for optimal health. Through the use of blog posts, fact sheets, posters and other educational materials, we hope we’re helping your clients and not being harmful in any way.
We recently encountered a disturbing use of one of our calorie-counting posters. Like many of our other products, we aim to educate and not shame our clients about their food choices. Similar to nutrition information being posted in fast food restaurants, the poster was created to bring awareness to the amount of exercise needed to use up calories consumed from various foods. Unfortunately, the posters were “stolen” at one facility by clients trying to further limit their calorie intake, who may have been suffering from eating disorders.
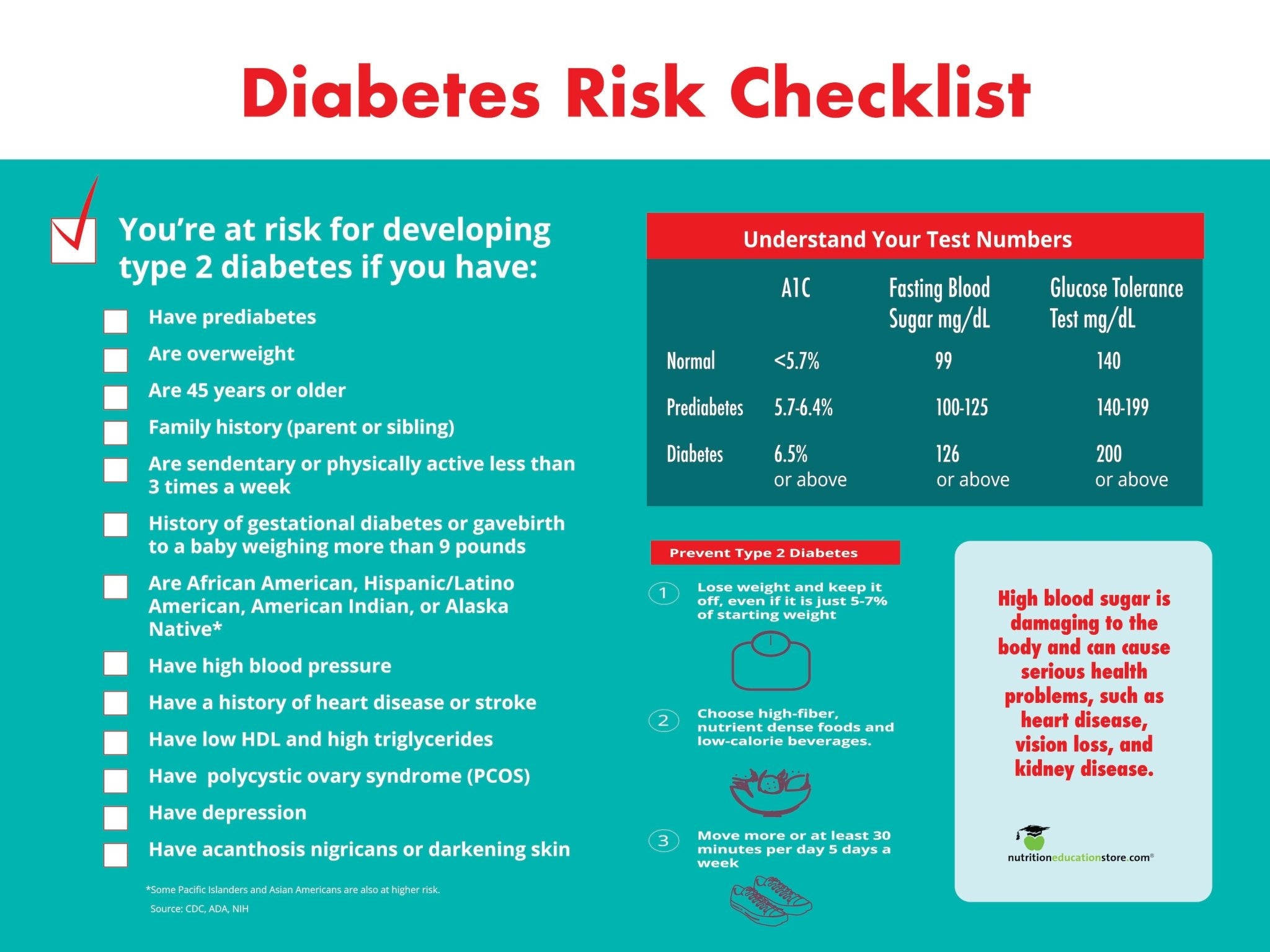
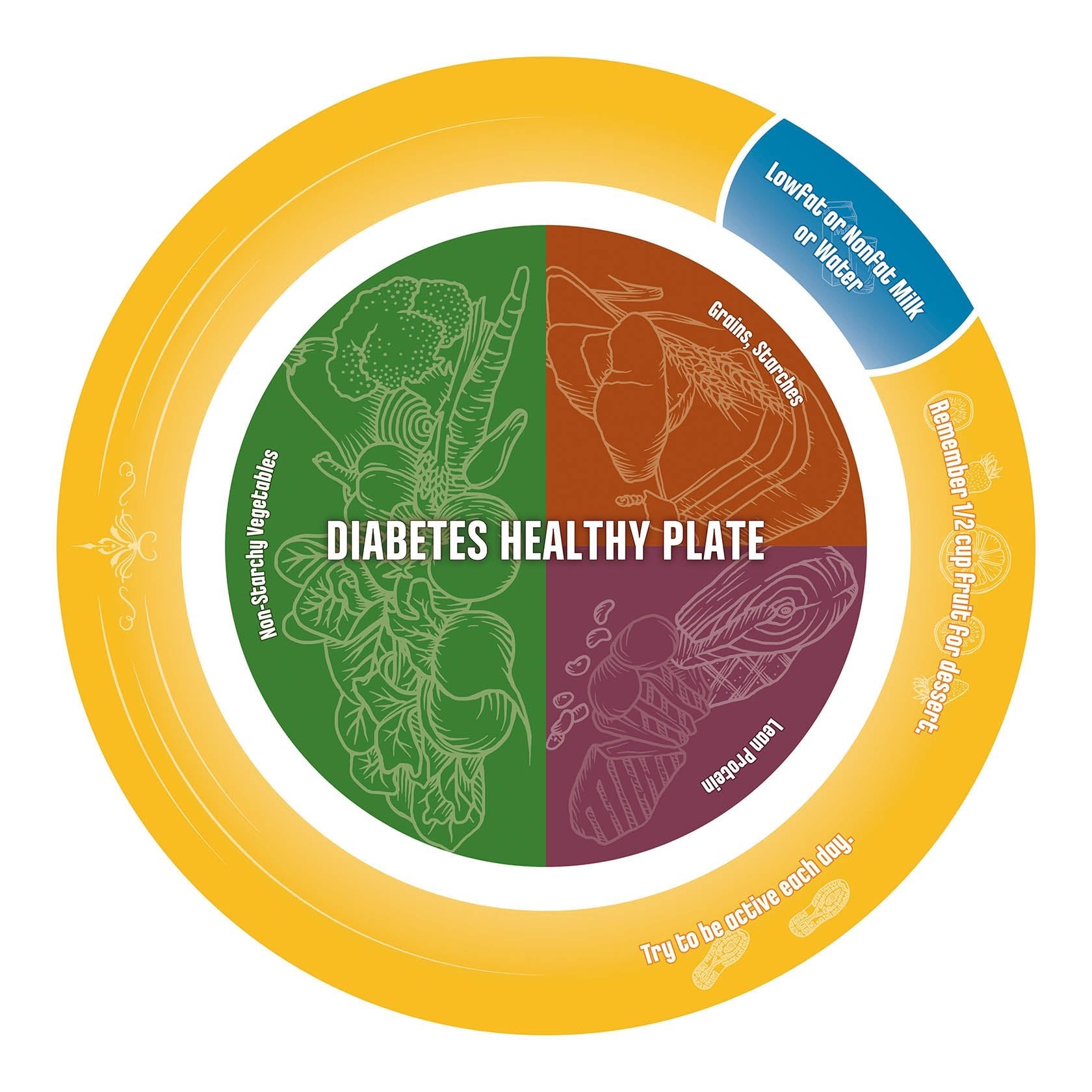
With over 70% of the US population being overweight or obese, our goal is to help reduce and manage chronic health conditions, several of which are weight-related. We recognize that eating disorders are also chronic health conditions that need to be addressed. These conditions are serious and can be life-threatening. Below are ways to spot them and refer clients to resources for more help.
Anorexia Nervosa:
The literal meaning of anorexia is “loss of appetite.” The term is frequently used in hospitals or nursing home settings to describe a person’s lack of appetite and could be related to depression, pain, nausea, or other conditions.
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is a completely different animal.
AN is listed in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, Volume 4 (DSM-IV) as a psychological condition characterized by a “refusal to maintain a bodyweight at or above a minimally normal weight for age and height, weight loss that leads to a weight below 85% of ideal and failure to gain expected weight during a period of growth leading to a weight below 8%% of expected weight.”
In addition, AN can affect someone who is fearful of gaining weight or becoming fat, despite being too thin. Body dysmorphia is also common in AN cases. Body dysmorphia happens when a person sees themselves as heavy when they’re actually underweight.
There are two sub-types of AN:
- Restricting type
- Binge-eating/purging type
A restricting person with anorexia will skip meals or eat very minimal amounts of food while a binge-eating/purging individual may binge/overeat then engage in purging behaviors such as vomiting, laxative use, or excessive exercise. 1
In addition to being malnourished, individuals with AN are at risk for bone loss, fractures, cardiac arrhythmias, amenorrhea and infertility. Individuals with purging behavior may develop esophageal and gastric damage, electrolyte abnormalities, dehydration, and damage to their colon if laxatives are abused.
Bulimia Nervosa:
Bulimia nervosa (BN) is also a mental and physical disease and is listed in both the DSM IV and V. Similar to anorexia, there is a binge-purge component where a person may overeat (binge) then compensate for the calories consumed through the use of vomiting, laxatives, diuretics, or excessive exercise.
In individuals with BN, these behaviors are observed: “repeated occurrence of binge eating which include both “eating within any 2-hour period, an amount of food that is definitively larger than what most individuals would eat in a similar time period under similar circumstances that includes a feeling that one cannot stop eating or control what or how much they are eating”.
In people with BN, this type of behavior can occur about twice a week for three months or even more frequently. Self-evaluation is critical and impacted by body shape and weight. The behavior can exist on its own and does not need to be coupled with anorexia nervosa.
A non-purging type of BN occurs when the person restricts food intake or fasts, but does not use self-induce vomiting or other purging behavior. Individuals with BN are at risk for the same physical damage that those with binge-purge anorexia may experience.
Binge Eating Disorder:
Binge-eating disorder is also considered an eating disorder, but it’s less physically damaging than AN or BN. Those with binge eating disorder tend to eat, in a discrete period of time (i.e.., within any 2-hour period), an amount of food that is much larger than most people would eat in a similar time frame under similar circumstances. They also feel a lack of control over eating (e.g., a feeling that they can’t stop eating or control what or how much they eat). 3
Binge eating occurrences have at least three of the following characteristics:
- Eating much more rapidly than normal
- Eating until feeling uncomfortably full
- Eating large amounts of food when not feeling physically hungry
- Eating alone because of feeling embarrassed by how much one is eating
- Feeling disgusted with oneself, depressed, or very guilty after overeating
The disordered eating happens at least 2 days of the week for 6 months and isn’t associated with purging behavior as mentioned above. Severity of the condition is dependent on the frequency of binge eating occurrences. Mild cases occur with 1 to 3 episodes weekly, while severe cases can include go up to 14 or more episodes in a week.
Individuals suffering from BN or binge-eating disorder may be normal weight, overweight, or obese. Risk for obesity, heart disease, and Type 2 diabetes are more common in binge eating disorder. Depression, anxiety, risk for suicide, and/or substance abuse may accompany any or all eating disorders. 4
OSFED
Other Specified Feeding/Eating Disorders (OSFED) are atypical and may include people who are overweight and not diagnosed. This website, sent by a reader, has more information.
How to Help Your Clients:
If your clients are suffering from any type of eating disorder, they need help from a team of professionals, including a medical doctor, psychologist or psychiatrist, and a registered dietitian. Registered dietitians can specialize in eating disorders and may carry the credential CDES (certified disordered eating specialist).5
To find an RDN who specializes in eating disorders, use this link: https://www.eatright.org/find-a-nutrition-expert-details
Eating disorders may be treated with medication, individual counseling, and/or group therapy. Family or other social support is critical in recovery.
When to refer clients for more help:
- Intentional weight loss with weight being under 85% of ideal or BMI of under 18.5.
- Persistent anxiety or depression surrounding eating
- Body dysmorphic syndrome
- Preoccupation with weight
- Intense fear of weight gain
- Binge-purge behavior or self-induced vomiting
- Refusal to eat
- Fasting or overly restricting food intake as a means of weight control
- Overtly thin appearance
- Excessive exercise
- Abuse of laxatives
- Extreme distress about binge eating
- Lack of control over eating behavior
By Lisa Andrews, MEd, RD, LD
Free Handout: Eating Disorder Handout

References:
- What is the DSM IV Diagnostic Criteria for Anorexia Nervosa – Eating Disorders
- O’Brien KM, Whelan DR, Sandler DP, Hall JE, Weinberg CR. Predictors and long-term health outcomes of eating disorders. PLoS One. 2017 Jul 10;12(7):e0181104.
- Table 21, DSM-IV to DSM-5 Binge Eating Disorder Comparison – DSM-5 Changes – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
- Claudat K, Brown TA, Anderson L, Bongiorno G, Berner LA, Reilly E, Luo T, Orloff N, Kaye WH. Correlates of co-occurring eating disorders and substance use disorders: a case for dialectical behavior therapy. Eat Disord. 2020 Mar-Apr;28(2):142-156.
- Klein DA, Sylvester JE, Schvey NA. Eating Disorders in Primary Care: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2021 Jan 1;103(1):22-32. Erratum in: Am Fam Physician. 2021 Mar 1;103(5):263.