Let’s get serious about dietary guidelines.
 The Dietary Guidelines for Americans are published jointly every 5 years by the U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) and Agriculture (USDA), as mandated by Congress. The goal of the Dietary Guidelines is to provide science-based nutrition and food safety recommendations for people two years and older to help promote habits that maximize good health and reduce the risk for chronic disease.
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans are published jointly every 5 years by the U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) and Agriculture (USDA), as mandated by Congress. The goal of the Dietary Guidelines is to provide science-based nutrition and food safety recommendations for people two years and older to help promote habits that maximize good health and reduce the risk for chronic disease.
Unfortunately, despite widespread efforts, eating habits overall remain largely unchanged. The majority of the population consumes too many refined grains, solid fats and added sugars, yet at the same time consumes too little fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. I find it disturbing that vegetable intake has actually declined since 2001-2004. Many young children consume the recommended amount of fruit and dairy, but these levels drop once they reach school age.
The 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee’s (DGAC) most recent recommendations outline what we can expect to see in the updated guidelines later this year. Overall, the dietary pattern recommended by the 2015 DGAC reaffirms the dietary pattern characteristics recommended by the 2010 DGAC. Let’s take a look at the highlights…
Over- and Underconsumption of Nutrients: Health Effects
 There is a continued emphasis on consuming a diet high in fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, all of which are good sources of the nutrients that continue to be underconsumed by the majority of Americans: vitamin D, calcium, potassium, and fiber. These foods are also low in the saturated fat and sodium that are typically overconsumed by Americans. Of interest, cholesterol is no longer considered a nutrient of concern.
There is a continued emphasis on consuming a diet high in fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, all of which are good sources of the nutrients that continue to be underconsumed by the majority of Americans: vitamin D, calcium, potassium, and fiber. These foods are also low in the saturated fat and sodium that are typically overconsumed by Americans. Of interest, cholesterol is no longer considered a nutrient of concern.
There is strong evidence that a high sodium intake increases risk of hypertension, leading the DGAC to continue to recommend decreasing sodium intake to 2,300mg per day. There is limited evidence of the value of reducing sodium intake further, or in terms of the role of potassium in hypertension. So make of that what you will.
The DGAC strongly states that people should discourage the consumption of low-fat or non-fat foods when the fat is replaced by refined carbohydrates or added sugars. The committee continues to recommend that less than 10% of a person’s overall daily calories should come from saturated fat, noting that replacing saturated fat with polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) reduces LDL-cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. There is strong evidence that replacing saturated fat with carbohydrates does not lower CVD risk, and there is limited evidence that replacing saturated fat with monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) leads to reduced CVD risk. Encouraging the use of non-hydrogenated vegetable oils including soybean, corn, olive and canola oils instead of animal fats or tropical fat is recommended instead of reducing saturated fat in the diet and increasing carbohydrate intake.
Instead of replacing fat with refined carbohydrates and added sugar, the recommendation is to increase nutrient-dense foods including whole grains, legumes, vegetables and fruit. It also includes increasing healthful sources of protein including legumes, nuts, low-fat dairy, and lean meats.
The DGAC recommends limiting added sugars to a maximum of 10 percent of total daily caloric intake. To meet this goal, sugar-sweetened beverages, which currently provide 39% of added sugars, should be replaced with unsweetened beverages.
Consumption Patterns and Plant-Based Foods
 What offers the most nutrient-dense diet? The guidelines explain that a diet that is based on vegetables, fruit, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and low-fat dairy, which includes more seafood and less red and processed meat, which is moderate in alcohol, and which contains low amounts of refined grains and sweetened foods and beverages provides the most nutrient-dense diet.
What offers the most nutrient-dense diet? The guidelines explain that a diet that is based on vegetables, fruit, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and low-fat dairy, which includes more seafood and less red and processed meat, which is moderate in alcohol, and which contains low amounts of refined grains and sweetened foods and beverages provides the most nutrient-dense diet.
The DGAC notes that there are several different diet patterns that follow these guidelines, including the Healthy U.S.-Style Pattern, the Healthy Vegetarian Pattern, and the Healthy Mediterranean-style Pattern. Each of these patterns provides more plant-based foods and lower amounts of meat than are currently consumed by the US population.
The committee notes that overconsumption of nutrients from foods and beverages, including fortified foods is rare. However, folate, calcium, iron, and vitamin D may be overconsumed when using high-dose supplements.
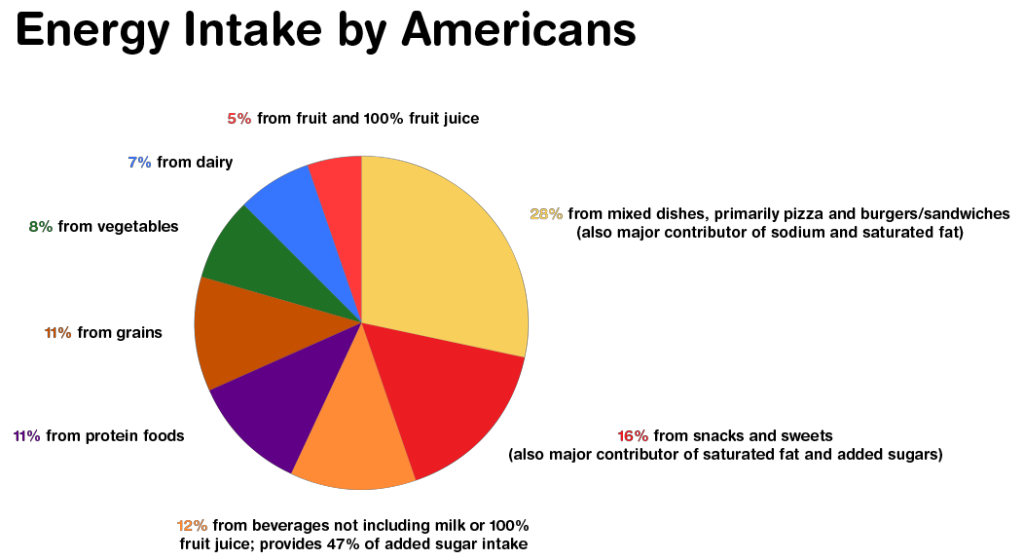
The information on the breakdown of energy intake is not surprising given the increase in overweight and obesity. Here’s a closer look at the breakdown of energy intake by Americans…
- 28% from mixed dishes, primarily pizza and burgers/sandwiches (also major contributor of sodium and saturated fat)
- 16% from snacks and sweets (also major contributor of saturated fat and added sugars)
- 12% from beverages not including milk or 100% fruit juice; provides 47% of added sugar intake
- 11% from protein foods
- 11% from grains
- 8% from vegetables
- 7% from dairy
- 5% from fruit and 100% fruit juice
The committee found that the majority of the population consumes three meals plus at least one snack, with adolescent females, young adult males, non-Hispanic Blacks, Hispanics, and individuals with lower incomes being the least likely to consume three meals a day. While breakfast tends to have a higher overall dietary quality compared to other meals and snacks, adolescents and young adults are the least likely to eat breakfast. Snacks contribute about 25% of daily energy intake, and unfortunately tend to be lower in important nutrients and higher in sodium, added sugars, and saturated fat.
It’s surprising that the USDA food patterns do not meet recommendations for potassium and vitamin D, and additional fortification strategies may be necessary to reach the RDA for vitamin D.
It’s well-known that rates of chronic disease are linked to overweight and obesity, playing a role in hypertension, CVD, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer, and that these weight-related illnesses now are present in children and adolescents who are overweight or obese. It’s not surprising that 90% of children with type 2 diabetes are overweight or obese.
Promoting Behavior Change
 I believe that more research and emphasis on promoting lasting behavior change is crucial, especially since the overall dietary choices haven’t changed significantly in the past 10 years. The DGAC suggests focusing on strategies that address:
I believe that more research and emphasis on promoting lasting behavior change is crucial, especially since the overall dietary choices haven’t changed significantly in the past 10 years. The DGAC suggests focusing on strategies that address:
- Reducing screen time, especially for children and adolescents to promote a healthy body weight as they transition into adulthood.
- Reducing the frequency of eating fast food for all age groups
- Increasing the frequency of family or shared meals
- Self-monitoring diet and physical activity behavior to promote lasting behavior change
- Effective food labeling to target healthier food choices
Food Environment
 The food environment is an area that requires more research to establish the most effective strategies to improve nutrition and health in schools and workplaces and to presents opportunities for RDs to collaborate with other groups to effect change.
The food environment is an area that requires more research to establish the most effective strategies to improve nutrition and health in schools and workplaces and to presents opportunities for RDs to collaborate with other groups to effect change.
The DGAC found strong to moderate evidence that multicomponent school and worksite policies are associated with improved dietary intake, including increased vegetable and fruit consumption and reduced body weight. Polices that include increased opportunities for physical activity, nutrition education, food service changes, and in schools (and parental involvement) are the most effective.
Food Safety and Sustainability
 The conversations around food safety and sustainability are often heated, with drastically opposing views. The DGAC recommends a moderate approach:
The conversations around food safety and sustainability are often heated, with drastically opposing views. The DGAC recommends a moderate approach:
- Both farmed and wild-caught seafood are nutrient-dense foods that are rich sources of healthy fatty acids. The risk of contamination is similar between farmed and wild caught seafood and does not outweigh the health benefits of consuming seafood.
- Wild-caught seafood cannot meet the growing demand, creating a need for sustainable seafood farming practices.
Caffeine Consumption
The research shows that in general, caffeine intake does not exceed recommend levels.
Moderate coffee consumption is considered to be 3-5 cups per day, or up to 400mg of caffeine per day. Moderate coffee consumption does not lead to increased health risk, and in fact is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, liver and endometrial cancer, and Parkinson’s disease. The DGAC agrees with the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Medical Association that until safety has been demonstrated, vulnerable populations including children, adolescents and young adults should avoid high-caffeine energy drinks or other products with high amounts of caffeine. Alcohol and energy drinks should never be mixed or consumed together.
Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should be cautious and adhere to current recommendations of the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and consume less than 200 mg caffeine per day (approximately two cups of coffee) to reduce risk of stillbirth, miscarriage, low birth weight, and small for gestational age.
Aspartame
 Aspartame is the football of sugar substitutes, going back and forth from being banned to considered a safe option. The DGAC concurs with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Panel on Food Additives that aspartame in amounts commonly consumed is safe and poses minimal health risk for healthy individuals without phenylketonuria (PKU). The risk to pregnant woman is unknown. However, long-term human studies are needed to assess a possible relationship between aspartame and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma. The recommendation is to stay below the aspartame Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of <50mg/kg/day. A 12-ounce diet beverage contains approximately 180mg aspartame. A 150-pound (68 kg) woman could drink up to 18 12-ounce diet beverages sweetened with aspartame and meet this guideline.
Aspartame is the football of sugar substitutes, going back and forth from being banned to considered a safe option. The DGAC concurs with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Panel on Food Additives that aspartame in amounts commonly consumed is safe and poses minimal health risk for healthy individuals without phenylketonuria (PKU). The risk to pregnant woman is unknown. However, long-term human studies are needed to assess a possible relationship between aspartame and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma. The recommendation is to stay below the aspartame Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of <50mg/kg/day. A 12-ounce diet beverage contains approximately 180mg aspartame. A 150-pound (68 kg) woman could drink up to 18 12-ounce diet beverages sweetened with aspartame and meet this guideline.
Anyway, that’s a collection of my immediate thoughts about the highlights from the latest DGAC update. What stood out to you? What most affects your practice?
By Lynn Grieger RDN, CDE, CPT, CWC

ALL-NEW Health/Nutrition Education Materials!
The Nutrition Education Store is overflowing with BRAND-NEW nutrition education materials. We have over 70 brand-new items that will make your life easier. Here are some of the latest and greatest…

Healthy Cooking Workbook

MyHealth Bulletin Board Kit

Quality Nutrition Poster Value Set
But wait, there’s more! Be sure to check out these amazing new products!
Displays by Design — NEW DISPLAYS

NEVER-BEFORE-SEEN Prizes and Rewards

BRAND-NEW Posters!

FRESH Handouts!

 When it comes to keeping your motivation through health and fitness challenges, sometimes a reward is just the boost you need. Establish what your reward will be ahead of time, and remember, the reward shouldn’t be food!
When it comes to keeping your motivation through health and fitness challenges, sometimes a reward is just the boost you need. Establish what your reward will be ahead of time, and remember, the reward shouldn’t be food!