It seems like lots of companies do biometric screenings for their employees these days. It’s a great way to give people a snapshot of their health. But knowing those numbers doesn’t help if they don’t understand what they mean. We have two handouts that can help – the Biometrics Screening Tool Handout Tearpad and the Printable Biometrics Form PDF.
On one side of these handouts, there’s space to record BMI, waist circumference, hemoglobin A1C, blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol (including total, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides). On the other side, there’s a glossary with easy-to-understand descriptions of each measurement.
Individual instructions or goals can be written in the space on the bottom left of side one. If you use the printable PDF form, you can add a logo or message before printing.
Here are 10 ideas for lessons and messages to use with the Biometrics Screening handouts:
- A biometric screening provides a snapshot of your health. These numbers tell where you’re doing well and areas that need attention.
- Manage these numbers by being more active, eating more lean protein, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, and eating less high fat, high sugar processed foods.
- If you’re missing any measurements, take the handout to your doctor and ask to have blood tests or other measurements done.
- Calculate your BMI using the formula on the handout, or search online for “BMI calculator” and plug in your height and weight. If your BMI falls in the overweight or obesity categories, losing even a relatively small amount of weight can improve your health.
- Waist circumference can tell you a lot, but many physicians don’t take this measurement. Use the instructions on this handout to measure your own waist circumference (or ask someone to help you). If it’s 40+ inches (for men) or 35+ inches (for for women), your risk of health problems such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease and high blood pressure increases.
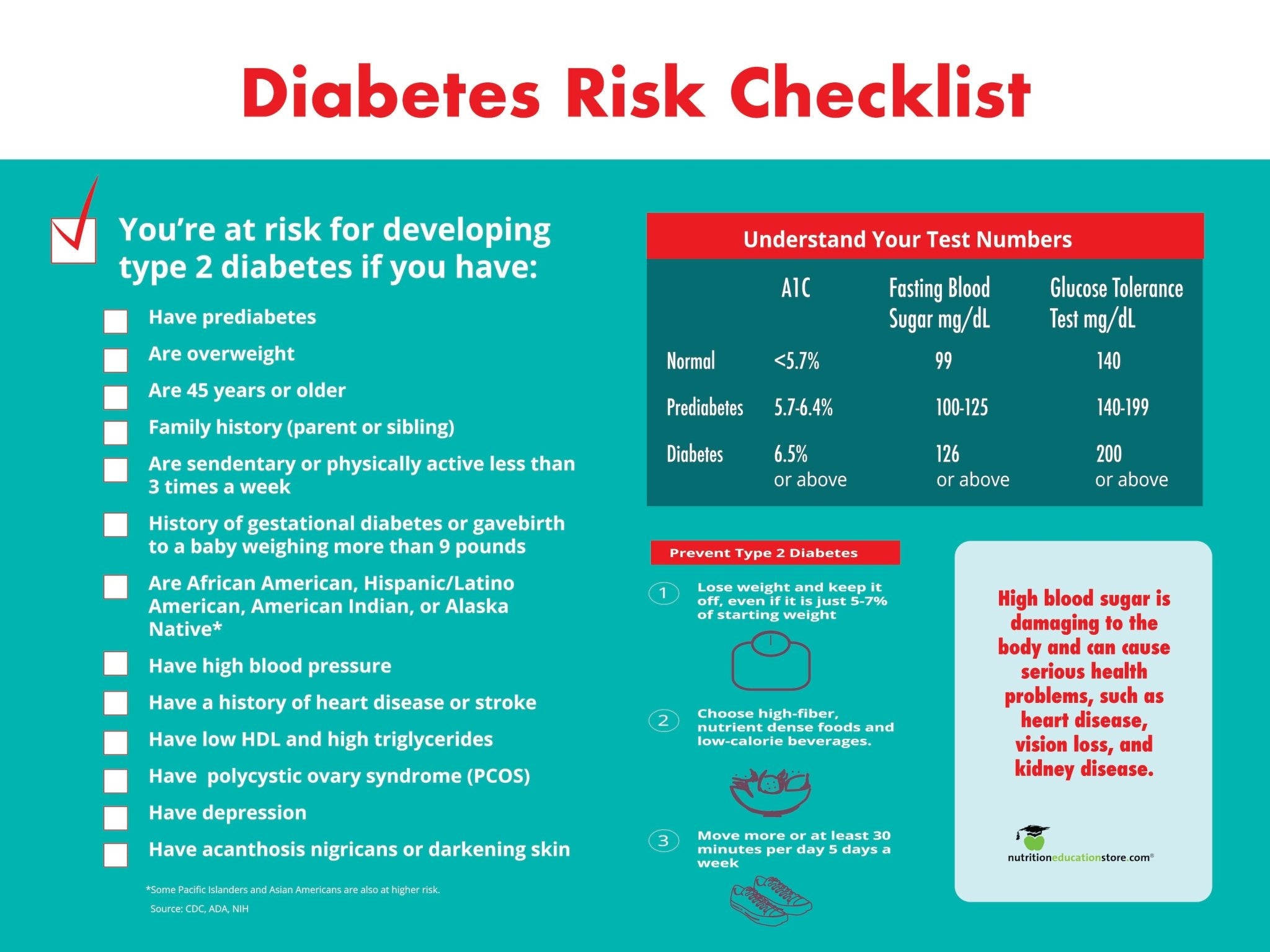
- Hemoglobin A1C measures your blood glucose (or blood sugar) over the past few months. Normal is less than 5.7%; prediabetes is 5.7% to 6.4%; and diabetes is 6.5% or higher. The higher the number, the greater your risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Blood glucose (or blood sugar) is sometimes measured after you’ve fasted. Normal is less than 100; prediabetes is 100-125; and diabetes is 126 or higher. If you haven’t fasted, a blood glucose of 200 or more indicates diabetes.
- Blood pressure measurements are given as two numbers (top is systolic, bottom is diastolic). Normal blood pressure is less than 120/80. If your blood pressure is above normal, check the categories on the handout to see where you fall.
- Cholesterol isn’t just one number! Keep track of your “good” cholesterol (HDL) and “bad” cholesterol (LDL), as well as triglycerides, which are a type of fat found in the blood.
- When your biometrics are out of the normal range, your risk increases for diseases like obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Knowing your numbers gives you something to track besides just a number on the scale.
Display our Measuring Your Biometrics poster or banner at health fairs and screenings. People can compare their biometric results to normal or optimal numbers based on recommendations from the American Diabetes Association, American Heart Association, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.