A recent study published in Clinical Nutrition looked at data from the PREDIMED study, which featured over 3,000 subjects with elevated risk for heart disease, but without type 2 diabetes. The study found that after 4 years, participants with the highest intake of legumes had a 35% reduction in risk for diabetes. The study was led by Jordi Salas-Salvadó from Rovira i Virgili University, University Hospital of Sant Joan de Reus, and Institute of Health Carlos III in Spain. Salas-Salvadó explained that substituting legumes, especially lentils, for other high-carbohydrate or high-fiber foods was linked with this reduction, though more research is needed to solidify the results.
In this prospective study, Salas-Salvadó and his team reviewed diet histories of diabetes-free subjects, both at the outset of the study and then annually for four years. Using regression models to estimate hazard ratios and confidence intervals, incidence of type 2 diabetes in the subjects was measured based on dietary intake. Compared to lowest intake of legumes (approximately 1 ½ servings per week), participants with the highest consumption (approximately 3 1/3 servings), had a 35% lower risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
The researchers compared types of legumes consumed and found that lentils in particular were linked with a 33% reduction in diabetes risk. This was observed with just one serving of lentils per week versus less than ½ serving. Chickpea consumption showed a smaller impact on lowering the risk of diabetes, while other dried beans and peas showed no significant link.
The authors suggest that substituting half a serving of legumes daily in place of a half serving of grains or high-protein foods (such as eggs or meat) may aid in reducing the risk for diabetes.
So, here are some simple ways to add more legumes to your eating pattern…
- Make lentil soup or chili
- Add cooked lentils to casseroles or salad
- Add chickpeas to soup or salad
- Make your own hummus from chickpeas or lentils
- Serve lentils as a side dish in place of rice or potatoes
By Lisa Andrews, MED, RD, LD
Reference:
Nerea Becerra-Tomás, Andrés Díaz-López, Núria Rosique-Esteban, Emilio Ros, Pilar Buil-Cosiales, Dolores Corella, Ramon Estruch, Montserrat Fitó, Lluís Serra-Majem, Fernando Arós, Rosa Maria Lamuela-Raventós, Miquel Fiol, José Manuel Santos-Lozano, Javier Diez-Espino, Olga Portoles, Jordi Salas-Salvadó Correspondence information about the author Jordi Salas-Salvadó Email the author Jordi Salas-Salvadó. “Legume consumption is inversely associated with type 2 diabetes incidence in adults: a prospective assessment from the PREDIMED study”. Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2017. 03.015
Study Link: http://www.clinicalnutritionjournal.com/article/S0261-5614(17)30106-1/abstract

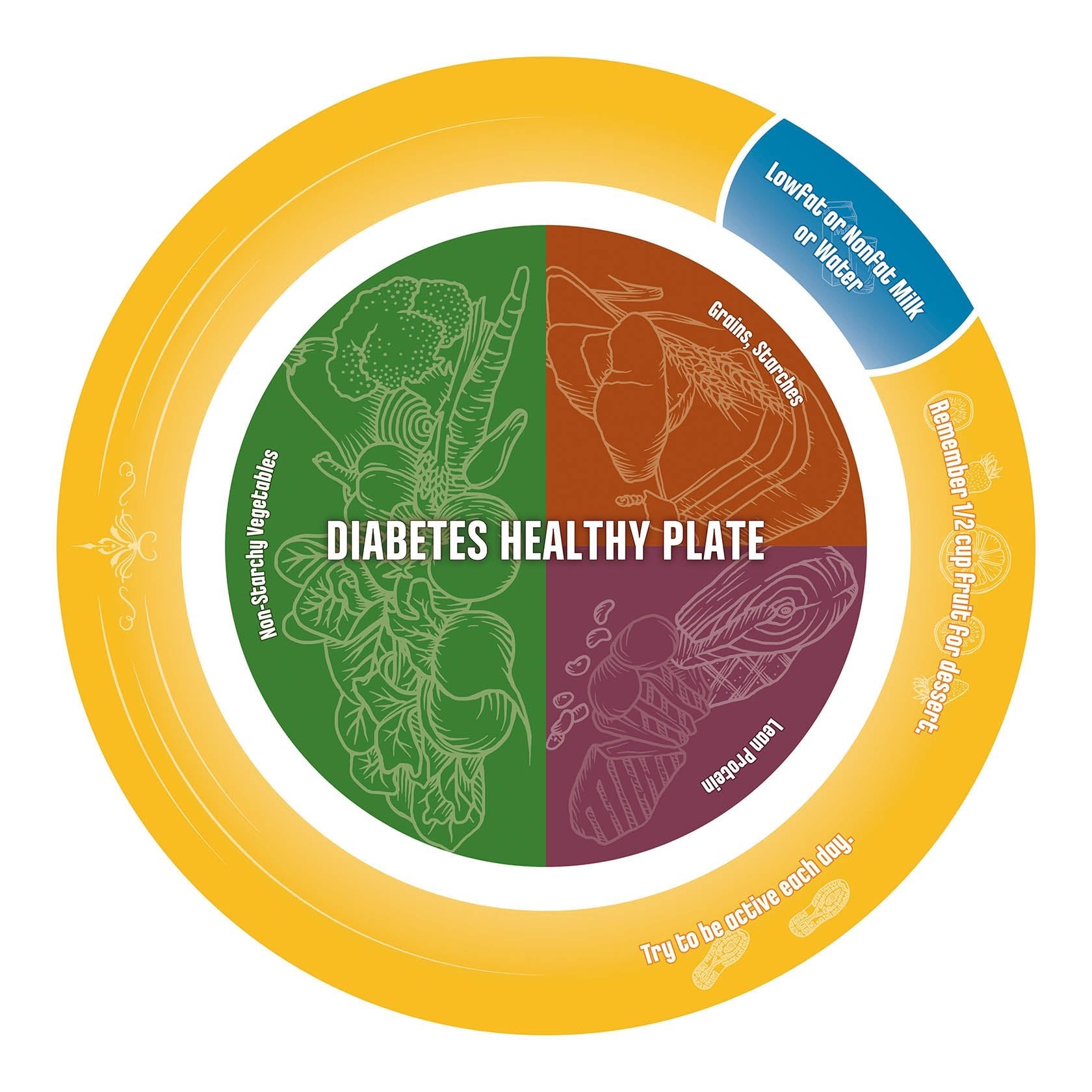
Diabetes Risk Banner and Banner Stand 24" X 67"
$125.00 $135.00
Add to Cart
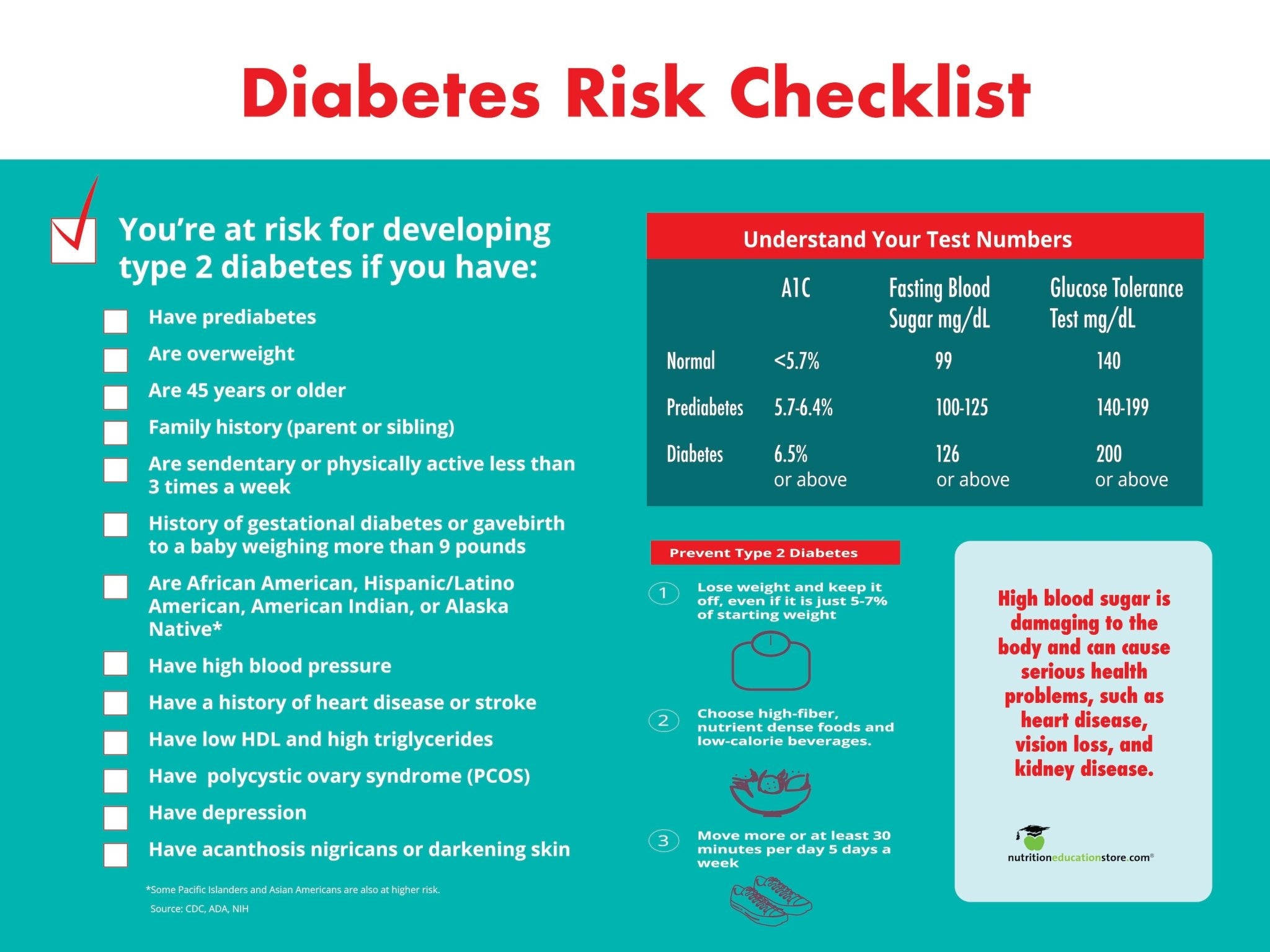
Diabetes Banner 48" X 36"
$88.00 $110.00
Add to Cart
New Products Available Now
Check out the Nutrition Nuggets page which features over 20% off three special products each week.
Connect with us on Google Plus