Have you seen the Sodium Math poster yet? We released it shortly after the Dietary Guidelines for Americans debuted earlier this year. It’s a fantastic resource for displays, presentations, and even simple office decoration. With engaging questions and alluring graphics, this poster teaches valuable lessons about salt in a memorable way.
Have you seen the Sodium Math poster yet? We released it shortly after the Dietary Guidelines for Americans debuted earlier this year. It’s a fantastic resource for displays, presentations, and even simple office decoration. With engaging questions and alluring graphics, this poster teaches valuable lessons about salt in a memorable way.
Of course, putting it together was no mean feat.
Today I want to walk through the process of creating this poster — I figured it would be useful for your own designs and displays. There were even 3 top lessons that we learned as we put the poster together! Plus, sodium is one of those food elements that most people don’t know enough about.
You see, once the latest edition of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans was officially released, I just knew that we had to create some kind of visual guide to dealing with sodium. But what? And how?
There’s always a lot of confusion about where sodium comes from in our daily diets. People hear the word “sodium” and they automatically equate that with “salt shaker.” However, the salt shaker is only responsible for a tiny amount of the sodium that most people consume each day. Most of the sodium (about 75%) comes from what is present in restaurant meals and packaged meals from the grocery store.
The Sodium Math poster is an engaging visual that shows how much sodium we are actually consuming versus how much is the maximum for good health.
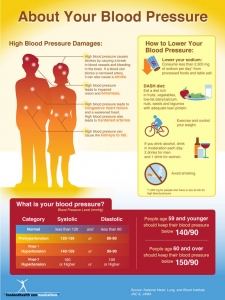
 It’s a bit of a shock to see the big pile of sodium that we eat each day and to see the teaspoons of sodium that each food contains! To balance that shock, the poster also showcases many fresh foods that are low in sodium. The poster clearly illustrates the lesson that a little work to eat 1,000 mg less sodium per day can make a big change in blood pressure.
It’s a bit of a shock to see the big pile of sodium that we eat each day and to see the teaspoons of sodium that each food contains! To balance that shock, the poster also showcases many fresh foods that are low in sodium. The poster clearly illustrates the lesson that a little work to eat 1,000 mg less sodium per day can make a big change in blood pressure.
This infogram poster was fun to work on and we learned a lot. Here are the top 3 lessons we learned in the making of this poster…
Lesson #1: True Sodium Content
One of the biggest shocks to us in the research was about how much sodium is in fast food. Turkey sandwiches sound healthy, but a turkey deli sandwich has 2,810 mg of sodium. That’s almost a 2 day supply!
Lesson #2: Planned Overs
After reading this poster, we devoted more effort to making “planned overs.” (That’s when we cook extra food for dinner and eat it for lunch the next day). Cooking your own meals at home can make a huge difference in your health, especially when it comes to sodium.
 Lesson #3: Small Shifts Are Important
Lesson #3: Small Shifts Are Important
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2015 recommend that just a small shift to lower sodium intake by 1,000 mg per day can make a positive impact on lowering blood pressure. This lesson was new to us and it seems relatively easy to implement. Plus, everyone loves an easy math lesson! We chose math because we wanted a way to explain sodium, salt, sodium intake, recommended sodium intake and changes needed, along with engaging food photos that can illustrate the whole lesson quickly.
So there you have it! A little peek behind the curtain and 3 lessons we learned while creating the Sodium Math poster.
As a special bonus, here’s a copy of one of our top printable sodium handouts! Reduce Salt has lots of tips and tricks for lowering the sodium in your diet. Get your free copy today!
And there are lots of other amazing sodium resources in the Nutrition Education Store! Here are a few fan favorites…

Salt DVD - Salt Video - Salt and Sodium Education - Nutrition Education DVD
$99.00 $99.00
Add to Cart